Gelatin Glue | A Natural Solution for Durable Bonds

Gelatin glue is one of the oldest adhesives known to humanity – its history dates back to ancient Egypt. Although the modern market is dominated by synthetic alternatives, this natural bonding agent is currently experiencing a renaissance – mainly due to growing environmental awareness and unique properties that modern chemical solutions cannot offer.
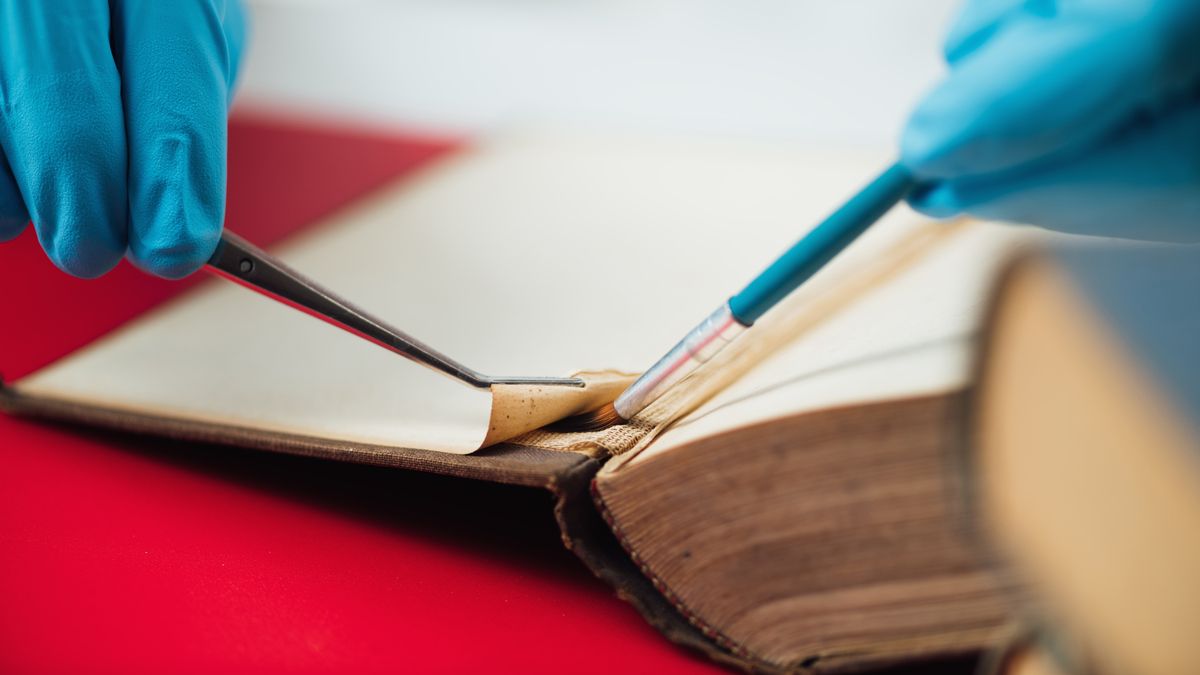
Gelatin glue finds applications in the printing industry, bookbinding, packaging production, and woodworking. Its reversibility, biodegradability, and adhesion to porous materials make it irreplaceable in many specialized applications. Where does it come from and how does it compare to synthetic adhesives? Read on to find out.
What Is Gelatin Glue?
Gelatin glue, also known as animal glue, is an adhesive obtained from natural collagen. Its main component is, of course, gelatin – a protein derived from bones, hides, cartilage, and tendons of farm animals, primarily pigs and cattle.
The production process of gelatin glue involves prolonged boiling of animal tissues in water. Through hydrolysis, the collagen contained in them transforms into soluble gelatin, which, after cooling, forms a colloid – a substance with adhesive properties.
Modern gelatin glues contain not only gelatin and water but also property modifiers, including plasticizers, sugars, salts, surfactants, and preservatives. Thanks to these additives, contemporary formulations significantly surpass the quality of simple gelatin-water mixtures used in the past.
History Of Gelatin Glue
The art of producing gelatin glue dates back to approximately 2000 BC.
Between 1500 and 1000 BC, gelatin glue was used in furniture production and wall paintings, which were even stored in the sarcophagi of Egyptian rulers. The Greeks and Romans, in turn, widely used this adhesive to repair damaged ceramics and to veneer wood.
Gelatin Glue In The 19th Century
The first American gelatin glue factory, founded by the Milwaukee Tanning Industry, was established in 1899.
However, L.D. Davis has a particularly interesting history – originally a stenciling company, the business pivoted to gelatin glue production during the Great Depression, selling to local box manufacturers and other industrial customers. This proved to be a brilliant move – the brand not only survived the economic crisis but actually flourished. Moreover, the original bookbinding glue formula developed by L.D. Davis is still produced unchanged to this day.
Properties Of Gelatin Glue
This natural adhesive stands out with a range of unique characteristics, which is why it remains a relevant solution in many industries. What specific properties of gelatin glue are we talking about?
Reversibility of bonds
A key property of gelatin glue is its reversibility. Unlike synthetic alternatives, bonds made with this adhesive can be reopened through the application of heat and moisture without damaging the bonded elements. Upon reheating, the substance returns to a plastic state, allowing for separation and repair.
This characteristic is particularly valued in lutherie and heritage conservation, as the ability to safely separate without damaging original materials is of fundamental importance in these fields.
Adhesion and strength
This adhesive exhibits excellent adhesion to porous materials such as wood, leather, and paper. The bonding strength of high-quality gelatin can reach up to 1.6 tons per square centimeter.
A significant advantage is its ability to adhere to itself even after hardening, which means that during repairs, a new layer can be applied directly over the old one and the elements can be clamped again. In the case of synthetic alternatives like PVA, it’s necessary to completely remove the old glue before repair, which often results in material damage.
Open time and application
The open time of gelatin glue is typically around one minute or less – this is the period during which the substance remains fluid and workable.
Bonding properties disappear when the temperature drops below 122°F (50°C). In practice, this means it’s necessary to heat the bonded elements and work in a warm room. For experienced craftsmen, this isn’t a problem, but it requires skill and precision.
Biodegradability
Gelatin glue is completely biodegradable – as a product of natural origin, it undergoes biological decomposition without leaving permanent environmental pollution. This is a significant advantage in times when manufacturers are seeking ecological alternatives to synthetic adhesives based on petrochemical resins.
Where Is Gelatin Glue Used?
This natural adhesive has a long tradition of use in various branches of industry.
- Bookbinding and printing industry
In bookbinding, gelatin glue finds application in the production of hardcover books, binders, luxury cardboard boxes, and game boards. Thanks to its high initial tack and the ability to precisely adjust working parameters (open time, viscosity, bonding strength), it performs excellently in fast production processes.
- Woodworking and furniture production
In woodworking, it’s used for joining wooden elements, veneering, and surface finishing. A characteristic feature of gelatin bonds is their controlled cracking—upon strong impact, the joint breaks only along the glue line without damaging the wood itself. In the case of PVA alternatives, cracks typically tear through the surrounding material, creating an irregular break that is much more difficult to repair.
- Packaging industry
Gelatin adhesives find wide application in the production of folding boxes with laminated edges. They also work excellently in puzzle manufacturing. Importantly, due to their exceptional properties, they can be used to bond very difficult materials, in some cases even with surface tension below 39 dynes.
Gelatin Glue vs. Synthetic Glues
The choice between natural animal glue and its synthetic alternatives depends on the project specifics and application requirements. Both solutions have their strengths and weaknesses, which are worth knowing before making a final decision.
What Speaks In Favor Of Gelatin Glue?
First and foremost, its natural origin and biodegradability. In times of growing environmental awareness, this is a significant argument – unlike synthetic alternatives based on petrochemicals, gelatin glue decomposes in the environment without leaving permanent pollution. Moreover, its production is relatively inexpensive, especially when manufacturers utilize recycled gelatin from pharmaceutical and food industry surpluses, thus transforming waste into valuable raw material.
The key advantage of this adhesive remains the reversibility of bonds. The ability to reopen joints through the application of heat and moisture, without damaging the bonded materials, is irreplaceable in heritage conservation, antique furniture restoration, and lutherie. Gelatin adhesive also demonstrates versatility in application, bonding effectively with a wide range of porous materials – from wood, through leather, to paper.
What Are The Limitations Of Gelatin Glue?
The biggest challenge is sensitivity to water and heat. High temperatures or humid environments can lead to weakening or complete loss of bonding properties. For this reason, gelatin glue is not suitable for outdoor applications or in high-humidity rooms.
Another limitation is the short open time, typically around one minute. This requires efficiency and experience, especially with complicated projects where precise element fitting takes more time. The application itself can also be demanding – the need to heat both the adhesive and the bonded elements can complicate the process and extend working time.
Gelatin glue is also susceptible to attack by microorganisms – bacteria, fungi, and insects can degrade it during storage, so it requires appropriate storage conditions. Finally, in terms of pure mechanical strength, it falls short of synthetic glues – epoxy or polyurethane bonds offer much greater bonding strength in applications requiring very durable, load-resistant joints.
When To Choose Synthetic Glues?
Modern chemical glues offer primarily greater mechanical strength, providing stronger and more durable bonds. Drying much faster than gelatin alternatives, they allow for more efficient work completion and shorter production time. A key advantage is also resistance to difficult environmental conditions – they handle moisture, temperature changes, and other external factors that are problematic for gelatin glue.
When To Choose Gelatin Glue?
This natural adhesive is the optimal choice when:
- you’re working with porous materials (wood, paper, leather),
- reversibility of bonds is important (conservation, lutherie),
- you care about an ecological and biodegradable solution,
- the project doesn’t require resistance to moisture and high temperatures,
- you value long tradition and a solution proven over centuries.
Gelatin glue | Summary
Gelatin glue, despite its centuries-old history, remains a current and valuable solution in many industries and crafts. Its unique properties – reversibility, biodegradability, adhesion to porous materials, and natural origin – make it irreplaceable in specialized applications.
From bookbinding and packaging production, through woodworking and lutherie, to the paper industry – gelatin glue proves that traditional solutions can compete with modern alternatives, especially where bond quality, repairability, and environmental concern matter.
In an era of growing environmental awareness, animal glue stands as an example of how natural products can find a place in modern, sustainable industry – combining centuries-old tradition with contemporary requirements.